English has many confusing word pairs, and bought or brought is one of the most common. Even good English speakers mix them up in daily conversation, writing, texts, and exams. The reason is simple: both words sound similar, both talk about getting something, and both are past tense verbs.
But here’s the good news 😊
Once you understand their meaning, difference, and correct usage, you will never confuse them again.
In this easy guide, you’ll learn:
- The clear meaning of bought and brought
- The key difference between bought and brought
- Simple rules to remember which word to use
- Real-life examples from school, shopping, and daily life
- Common mistakes and how to avoid them
This explanation is written in plain English, so even a 4th-grade student can understand it easily.
What Does Each Word Mean?
Let’s start with the basic meaning of each word.
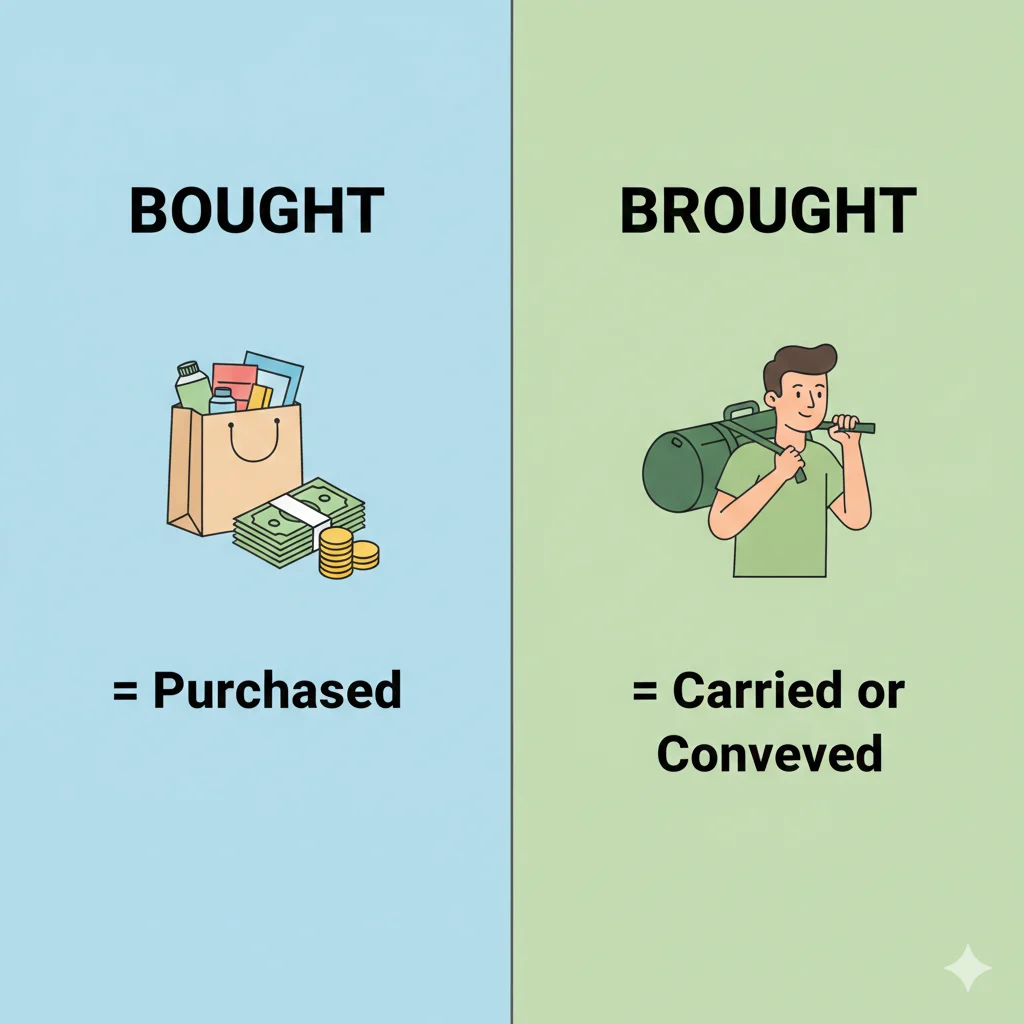
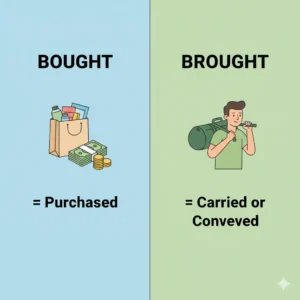
Meaning of Bought
Bought means to purchase something.
It is the past tense of “buy.”
👉 If money is involved, the correct word is bought.
Part of Speech: Verb (past tense)
Easy Examples of Bought
- I bought a new pencil from the shop.
- She bought a dress for the party.
- We bought ice cream after school.
🧠 Simple story to remember:
If you go to a shop and pay money 💰, you bought something.

Meaning of Brought
Brought means to carry or take something from one place to another.
It is the past tense of “bring.”
👉 If you carry something with you, the correct word is brought.
Part of Speech: Verb (past tense)
Easy Examples of Brought
- I brought my lunch to school.
- She brought her friend to the party.
- He brought his book from home.
🧠 Simple story to remember:
If you move something from there to here, you brought it.
The Key Difference Between Bought and Brought
Many learners ask: What is the difference between bought and brought?
Here is the easiest way to understand it.
Bought vs Brought Comparison Table
| Feature | Bought | Brought |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Purchased something | Carried something |
| Past tense of | Buy | Bring |
| Money involved? | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Action | Paying and owning | Moving or carrying |
| Example | I bought a toy. | I brought a toy. |
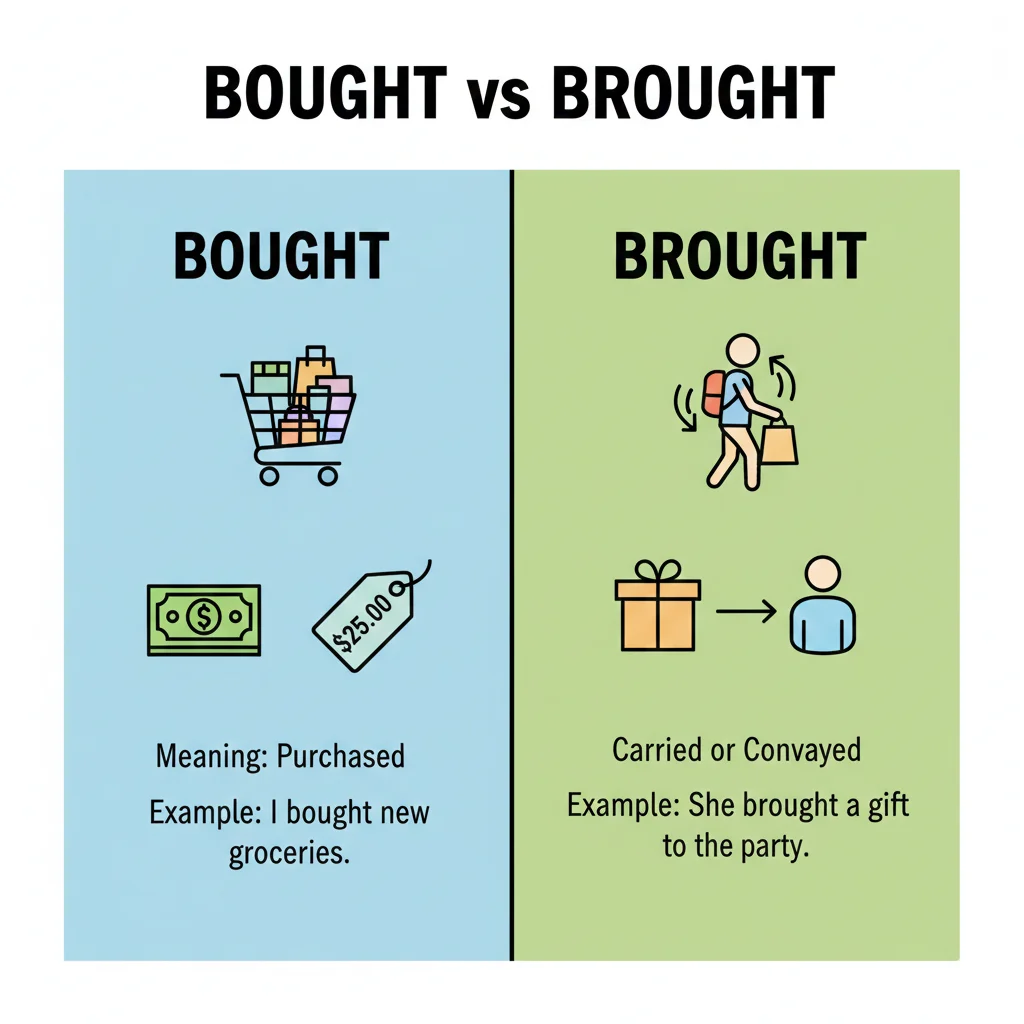
Quick Tip to Remember
- Bought → Buy → Money 💰
- Brought → Bring → Carry 👜
If money is used → Bought
If movement is used → Brought
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even native speakers make mistakes with bought or brought. Let’s fix them.
❌ Common Mistake 1
Incorrect: I brought a new phone yesterday.
Correct: I bought a new phone yesterday.
✅ Why?
You paid money for the phone, so use bought.
❌ Common Mistake 2
Incorrect: She bought her book to school.
Correct: She brought her book to school.
✅ Why?
She carried the book from home, not purchased it.

❌ Common Mistake 3
Incorrect: He brought groceries from the store.
Correct: He bought groceries from the store.
✅ Why?
Groceries are purchased, so bought is correct.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
Ask yourself one question:
👉 Was money used?
- Yes → Bought
- No → Brought
When to Use Bought
Use bought when you talk about shopping, paying, or purchasing.
Situations Where “Bought” Is Correct
- Shopping at a store
- Online purchases
- Gifts you paid for
- Anything that costs money
Easy Example Sentences
- I bought a notebook for my class.
- Mom bought fruits from the market.
- They bought tickets for the movie.
- He bought a gift for his sister.
- We bought a new chair for our room.
📌 Real-life tip:
If you can ask, “How much did it cost?” → use bought.
When to Use Brought
Use brought when you talk about carrying or taking something from one place to another.
Situations Where “Brought” Is Correct
- Carrying items
- Taking people along
- Moving things from home to school
- Bringing food, books, or gifts
Easy Example Sentences
- I brought my water bottle to school.
- She brought her brother with her.
- He brought flowers for his mother.
- We brought snacks for the trip.
- They brought their homework today.
🧠 Memory Hack:
Brought has “R-O-U-G-H-T” like “through” → movement
Quick Recap: Bought vs Brought
Let’s make it super simple 👇
- Bought = Purchased something (money involved)
- Brought = Carried something (movement involved)
- Bought → Buy → 💰
- Brought → Bring → 👜
If you remember this, you’ll never confuse them again.
Advanced Tips
Word Origin (Simple)
- Bought comes from the old word bycgan (to purchase).
- Brought comes from bringan (to carry).
In Exams and Formal Writing
Teachers often mark bought vs brought as a common grammar mistake.
Using the wrong word can change the meaning of the sentence.
Example:
- I bought lunch. (You paid for it)
- I brought lunch. (You carried it)
In Texting and Online Writing
Wrong usage can confuse readers:
- “I brought a phone” ❌
- “I bought a phone” ✅
Clear words = clear meaning.
Mini Quiz: Test Your Understanding
Fill in the blanks with bought or brought.
- She ______ a cake for the party.
- I ______ my umbrella because it was raining.
- He ______ new shoes yesterday.
- We ______ snacks to the picnic.
- Mom ______ vegetables from the market.
- They ______ their dog to the park.
Answers:
- bought
- brought
- bought
- brought
- bought
- brought
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between bought and brought?
Bought means purchased with money. Brought means carried from one place to another.
2. Is bought related to buy?
Yes. Bought is the past tense of buy.
3. Is brought related to bring?
Yes. Brought is the past tense of bring.
4. Can bought and brought be used in the same sentence?
Yes.
Example: I bought a gift and brought it home.
5. Why do people confuse bought and brought?
Because they sound similar and both are past tense verbs.
Conclusion
Now you clearly know the difference between bought or brought.
Bought is about paying money, and brought is about carrying something. With simple rules, real-life examples, and memory tricks, this confusing grammar pair becomes easy.
The key is practice. Read sentences, speak slowly, and ask yourself:
👉 Did I pay for it or carry it?
Every small step improves your English. Keep learning, keep practicing, and soon these mistakes will disappear 😊

Caribbean-born novelist Jean Rhys (1890–1979) explored alienation, identity, and female psychology with lyrical, haunting, and emotionally rich prose.