Have you ever written “engrained” when you really meant “ingrained” and wondered if it was correct? You are not alone. These two words sound almost identical, which makes them tricky even for fluent English speakers. While they may seem interchangeable at first glance, they have distinct meanings and are used differently in sentences. Choosing the wrong one can slightly—or even completely—change what you mean.
In this complete guide, we will explain the difference between ingrained vs engrained in simple, easy-to-understand language. You will learn what each word really means, when to use each, common mistakes to avoid, and how to remember them easily. Plus, you’ll see plenty of real-life examples from school, daily life, and writing situations. By the end of this article, you will never confuse these words again.
What Does Each Word Mean?
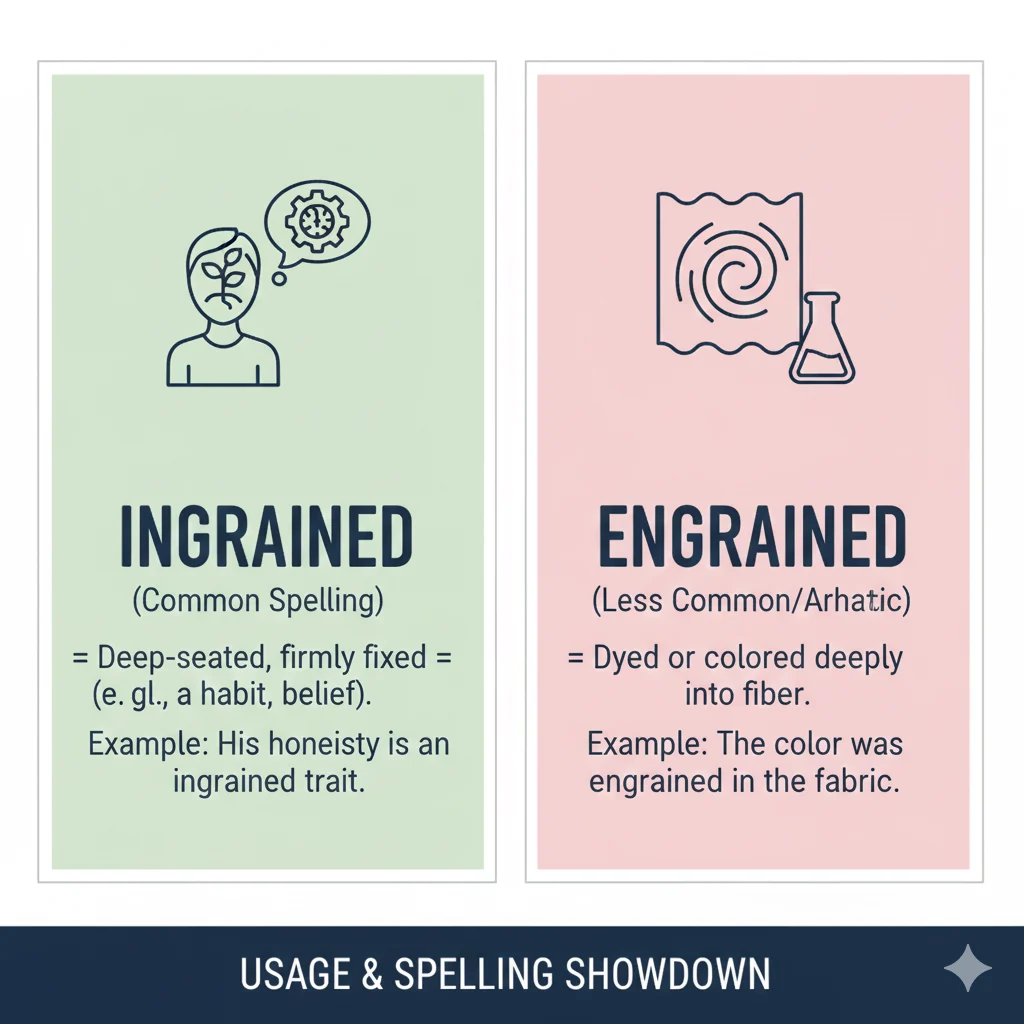
Ingrained
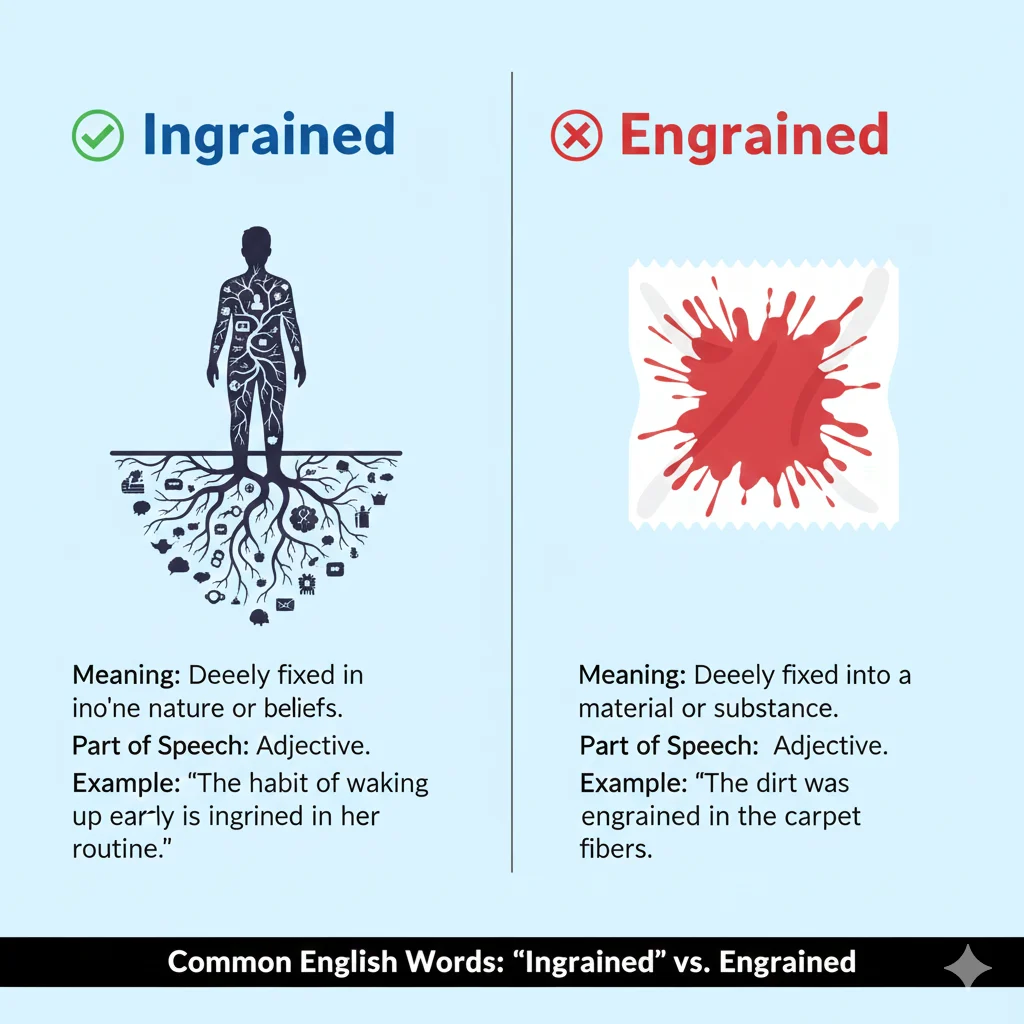
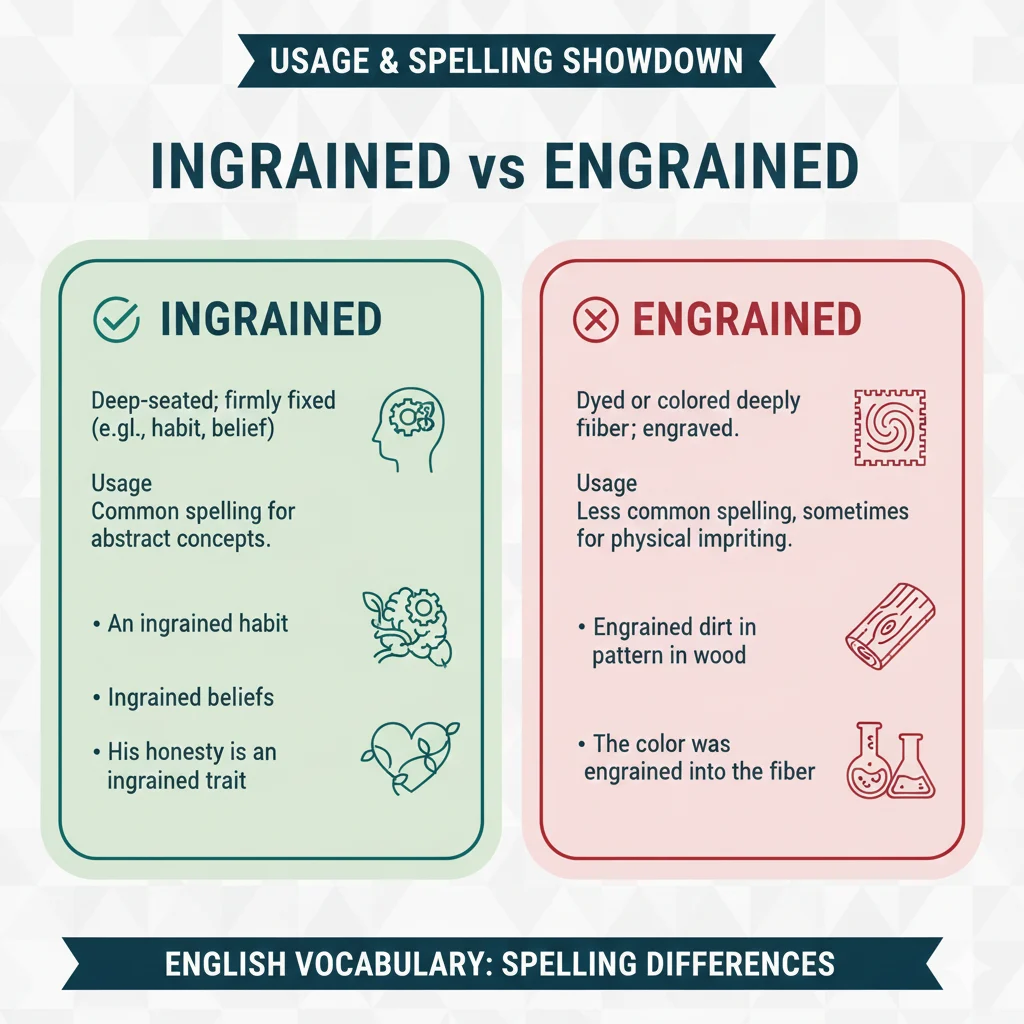
Meaning: The word ingrained refers to something that is firmly established or deeply fixed, especially in a person’s habits, beliefs, or character.
Part of Speech: Adjective
Examples:
- Reading every day has become an ingrained habit for Maria.
- His fear of dogs was ingrained from early childhood experiences.
- Honesty and kindness are ingrained in their family values.
Mini Story: Imagine a tree with deep roots. No matter how strong the wind blows, the tree stays upright because its roots are ingrained in the soil. Similarly, an ingrained habit stays with you no matter what happens.
Memory Tip: Think of “in-grain.” Something in the grain of a person’s life is deeply fixed and difficult to change.
Engrained
Meaning: The word engrained is an older or less common spelling of “ingrained.” Historically, it also refers to dye or color that has penetrated fabric deeply, or designs carved into a surface.
Part of Speech: Adjective
Examples:
- The red dye was engrained in the fabric and would not wash out.
- Some old customs are engrained in the village culture.
- The engrained carvings on the stone wall told the story of the past.
Mini Story: Imagine engraving your name into a piece of wood. It is permanent and cannot easily be removed. Similarly, an engrained habit or color is fixed and difficult to change.
Memory Tip: Think of engraving, something permanently fixed into a surface.
The Key Difference Between Ingrained and Engrained
While these words are often used interchangeably, subtle differences exist:
| Feature | Ingrained | Engrained |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Deeply rooted habits, beliefs, or personality traits | Can mean deeply fixed OR dye/color penetrated in fabric |
| Usage | Standard modern English; widely used | Less common; mainly British English or historical contexts |
| Part of Speech | Adjective | Adjective |
| Examples | Ingrained habit, ingrained fear | Engrained dye, engrained tradition |
| Quick Tip | Use ingrained for habits, personality, or ideas | Use engrained for fabrics, dyes, or historical texts |
Quick Tip: When talking about habits, behavior, or beliefs, always use ingrained. When talking about fabric, dye, or engraving, engrained can be correct.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Using “engrained” for everyday habits
- Incorrect: Laziness is engrained in his personality.
- Correct: Laziness is ingrained in his personality.
Why: People confuse the spelling, but “ingrained” is the standard choice for personality traits or habits.
Mistake 2: Confusing historical or fabric-related usage
- Incorrect: The tradition was engrained in the town.
- Correct: The tradition was ingrained in the town.
Why: Unless you are talking about dye, fabric, or an old-fashioned context, stick to “ingrained.”

Mistake 3: Using “ingrained” in dye-related contexts
- Incorrect: The red color was ingrained in the fabric.
- Correct: The red color was engrained in the fabric.
Why: “Engrained” is correct when referring to color or dye penetrating fabric deeply.
When to Use Ingrained
Situations:
- Personality traits
- Habits and routines
- Beliefs or fears
- Traditions and culture
Examples:
- Good manners should be ingrained in children from a young age.
- Her fear of public speaking is deeply ingrained.
- Checking your phone first thing in the morning can become an ingrained habit.
- Respect for elders is ingrained in many cultures.
- Volunteering and helping others became ingrained in her daily routine.
Real-life Tip: If it describes a behavior or idea that stays with someone for a long time, use ingrained.
When to Use Engrained
Situations:
- Fabric, dye, or color penetration
- Carvings, patterns, or engravings
- Historical British English usage
- Literary or formal texts
Examples:
- The red dye was engrained in the cloth and would not fade.
- The engrained carvings on the wall showed scenes from the past.
- Some old expressions are still engrained in British literature.
- The engrained ink on the certificates made them permanent.
- Historical records show engrained traditions in the town.
Memory Hack: Picture engraving — something carved or fixed in a surface that lasts a long time.
Advanced Tips
- Origin of Words:
- Ingrained comes from Middle English “en” + “grain,” meaning something fixed deeply in the grain (habit, idea).
- Engrained is related to “engrave”, historically used for fabric dye, color, or carvings.
- Formal Writing: Always prefer ingrained for habits, behavior, or ideas in essays, reports, or exams.
- Online/Informal Writing: Using “engrained” instead of “ingrained” may confuse readers; stick to modern spelling.
- British vs American English: American English rarely uses “engrained,” except in specific historical or literary contexts.
Real-Life Mini-Stories to Remember the Difference
- At School: Tom has an ingrained habit of doing homework as soon as he gets home. His desk is covered with books, so this habit is easy to see.
- At Home: Mom dyed a red shirt last week. The color is engrained in the fabric — even after washing, it didn’t fade.
- At Work: Jane’s habit of double-checking emails is ingrained, so she never misses an important message.
- In Literature: In old British novels, you may find phrases that are engrained in the story’s historical setting.
Quick Recap: Ingrained vs Engrained
- Ingrained: Deeply rooted in habits, personality, or beliefs.
- Engrained: Rare spelling, often for fabric dye, engravings, or historical contexts.
- Tip:
- Habit, idea, personality → ingrained
- Fabric, dye, engraving → engrained
- Both words are adjectives.
- Memory hack: “In-grain” = habit; “Engraving” = fixed in surface.
Mini Quiz
Fill in the blanks with ingrained or engrained:
- Honesty is ________ in her character.
- The red dye was ________ in the cloth.
- Fear of spiders is ________ from childhood.
- The engravings were deeply ________ in the stone.
- Respect for teachers should be ________ in students.
- Bad habits can be ________ if not corrected early.
- The engrained ink on old certificates made them permanent.
(Answers 1.ingrained, 2. engrained, 3. ingrained, 4. engrained, 5. ingrained, 6. ingrained, 7. engrained)
FAQs
1. Can “engrained” be used instead of “ingrained”?
Yes, but modern English prefers ingrained for habits, ideas, or personality traits.
2. Which word is correct in American English?
Ingrained is correct in almost all modern American English contexts.
3. Are these words verbs?
No, both are adjectives.
4. How do I remember the difference?
Think: “Ingrained” = habits or ideas; “Engrained” = fabric, dye, or engraving.
5. Can “engrained” appear in historical texts?
Yes, it appears in British English or older literary works, especially related to fabrics or engravings.
Conclusion
Now you have a clear understanding of ingrained vs engrained. Ingrained is the go-to word for habits, beliefs, routines, or personality traits. Engrained is less common and often used when talking about fabrics, dyes, engravings, or historical contexts. By practicing these examples and remembering the mini-stories, you’ll confidently avoid common mistakes and choose the correct word every time.
English is full of tricky words, but guides like this make them easy to master. Keep practicing, read actively, and pay attention to how these words appear in books, essays, and daily conversations. Soon, choosing the right word will become natural. Every small step improves your English — and learning is always exciting!

Caribbean-born novelist Jean Rhys (1890–1979) explored alienation, identity, and female psychology with lyrical, haunting, and emotionally rich prose.